Concepts
Sea Water
properties
Average consumption of fresh water by each crew member personally is 100 litres/day. Moreover, water needs for machinery operation and service. In a large tanker vessel having cargo oil pumps, ballast pumps, generator driven by steam turbines the auxiliary boiler consumption per day can be more than 30 tonnes.
Sufficient fresh and potable (drinking) water can be taken from a shore supply when the vessel in port or a barge when at anchorage to ensure crew and passenger requirements. But water for engine room machinery operation and service usually generates from sea water by means of fresh generator plant installed on board.
Well known facts that sea water cannot be able to drink, domestic or technical use on ship due to high salinity and hardness. The last one cause strongly scaling formation during heating. That is one of the main reasons which exclude it utilization in high temperature cooling and feed water systems.
Sea water contains salts with concentration on average 3.5 % or 35 ‰. In another way in 1 kg of sea water dissolved 35 g of different salts. The main part belongs to NaCl salt around 80 %. In ship documentary (guides, manuals etc.) the SW salinity characterised by chloride content and defines in ppm.
FW generation ways
There are two ways of freshwater generation:
1) freshwater generation without water phase conversion
2) freshwater generation with intermediate water phase conversion into solid or gas (vapours).
To the first way belongs next methods: chemical, electrochemical and reverse osmosis. To the second way: freezing and distillation.
From the mentioned above methods of freshwater generation the most essential on vessels are distillation and reverse osmosis.
In the figure below shown sea water structure according to the theory of electrolytic dissociation (Arrhenius theory of dissociation).
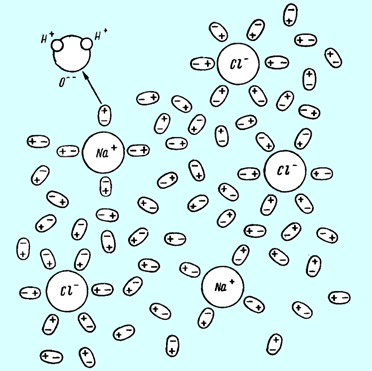
Sea water structure
Sea water contains Na+ and Cl- ions. Each of them surrounded by water molecules. These H2O molecules create hydrate covering of ion. At the same time other molecules free (around 90 % of all molecules amount).
If non free molecules in solution that this solution is saturated.
The molecules of hydrate covering holds near ion by electrostatically attraction forces.
Ions and hydrate cover creates a complex termed as solvate. Solvate sizes the higher order than H2O molecules. They are bulky, more heavy and less mobile. This feature is the basic of most effective freshwater generation methods.
During heating a water separate free molecules due to thermal movement rich a high speed that help it to relive from intermolecular tension forces and fly out through the interface between water and vapor. Ofcourse less mobile solvates can’t rich the same high speed as free molecules and overpass the intermolecular tension forces. That is why the interface function as a filter which water molecules overpass but can’t pass ions of solute salts.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a process commonly used in freshwater generation or boiler feed-water desalination. RO relies on the principle that when solutions of differing concentrations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, water from the less concentrated solution passes through the membrane (figure a) until the concentrations of both solutions are equalised. A hydraulic pressure gradient thus builds up across the membrane. The process will continue until the hydraulic gradient is equal to the osmotic pressure (figure b). This is determined by the difference in concentration between the two solutions. If a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure is applied to the more concentrated solution, the process is reversed (figure c). Water from the more concentrated solution is forced back through the semipermeable membrane diluting the more dilute solution on the other side (figure d). The concentration of the stronger solution is thus increased. Water from the dilute side of the membrane passes to FW storage while that from the concentrated side is either run to waste as brine. RO method is capable of removing up to 90% of dissolved solids depending upon the age of the plant.


a b


c d
Schematic of reverse osmosis process
a – osmosis process, b – osmotic pressure building, c – beginning of reverse osmosis process, d – end of the reverse osmosis process: 1 – freshwater 2 – saltwater 3 – membrane
FWG classification
All FWG plants can be divide on three types: boiled, adiabatic and membrane type.
The main practical utilization on marine vessels nowadays has distillation method of freshwater generation by means of engines waste heat recovery with boiled type FWG plant. Also, except boiled type FWG plants due to high capacity and efficiency on board of cruise liners installs membrane type RO FWG plants. While FWG adiabatic type didn’t find utilization on bord of marine vessels.
Classification of FWG plant boiled type with distillation method of FW generation can be done on the basis of:
1) Heat exchanger design – shall-and-tube or plate type
2) Heating medium – engine jacket water or steam
3) Pressure inside evaporator – pressure or vacuum type
FWG plant membrane type can be classified depend on number
of passes for increasing freshwater quality – one pass, two pass or multi pass
